What are Cavities?
Definition of Cavities
Cavities are the destruction of the tooth’s enamel, the hard, outer layer of the teeth. They occur when harmful bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, creating tiny openings or holes.
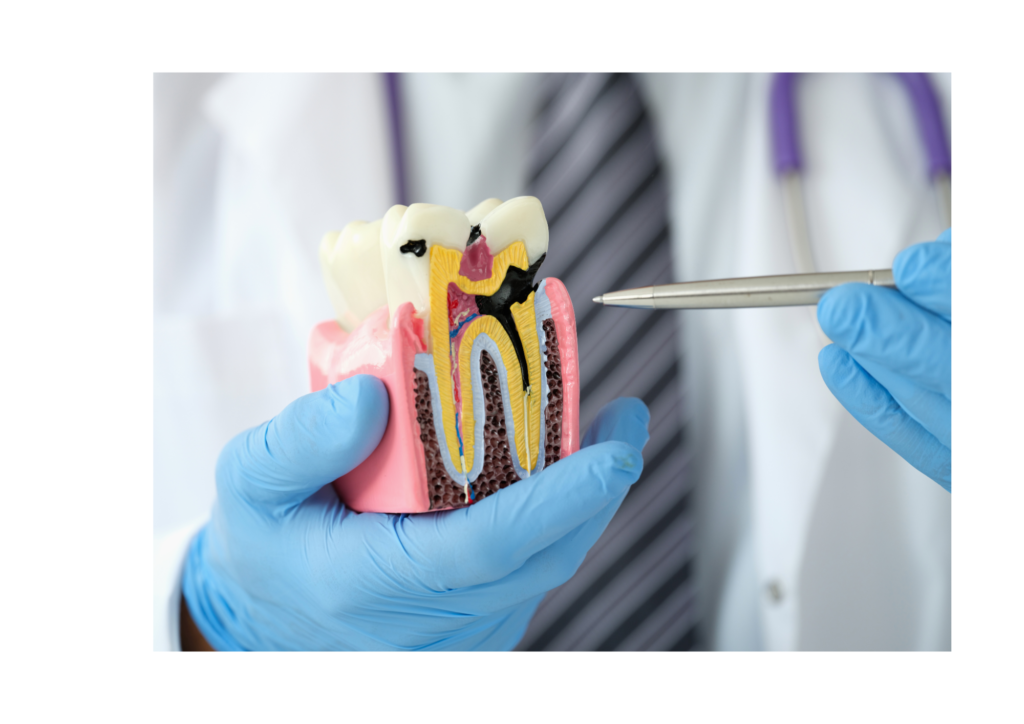
How Cavities Form
Cavities form when the bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and starches from food, producing acids as a byproduct. These acids gradually dissolve the minerals in the enamel, leading to the formation of cavities.
Causes of Cavities
Bacteria in the Mouth
The primary culprits of cavities are the bacteria that naturally reside in the mouth. Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus are among the most common bacteria associated with cavities.
Sugary and Acidic Foods
Consuming sugary and acidic foods and beverages, such as candies, sodas, and fruit juices, provides fuel for the bacteria, leading to the production of harmful acids.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting oral hygiene practices like regular brushing and flossing allows plaque to build up on the teeth, creating an environment where bacteria can thrive.
Dry Mouth
Saliva helps to wash away food particles and neutralize acids. A dry mouth, caused by certain medications or medical conditions, can increase the risk of cavities.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can contribute to an increased risk of cavities.
Signs and Symptoms of Cavities
Toothache
One of the earliest signs of cavities is a persistent toothache, which can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Sensitivity
Teeth affected by cavities often become sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages.
Visible Holes or Pits
As decay progresses, visible holes or pits may appear on the surface of the teeth.
Staining on Teeth
Dark spots or stains on the teeth can indicate the presence of cavities.
Pain When Eating or Drinking
Cavities can cause sharp pain when eating or drinking, especially when consuming sweet, hot, or cold items.
Diagnosis of Cavities
Dental Examination
Dentists can detect cavities during a routine dental examination by visually inspecting the teeth and using dental instruments to probe for soft spots.
X-rays
Dental X-rays can reveal cavities that are not visible to the naked eye, especially those between teeth.
Cavity Detection Dye
Some dentists use a special dye that stains decayed areas, making it easier to identify and treat cavities.
Prevention of Cavities
Regular Brushing and Flossing
Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are fundamental practices for preventing cavities.
Use of Fluoride
Fluoride strengthens the enamel and makes it more resistant to decay. Using fluoride toothpaste and drinking fluoridated water can help protect your teeth.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet that limits sugary and acidic foods and includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and dairy products can promote dental health.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Visiting the dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups allows for early detection and treatment of cavities.
Dental Sealants
Dental sealants are protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth, where cavities often form. They can help prevent decay in these vulnerable areas.
Treatment Options for Cavities
Fluoride Treatments
In the early stages of cavities, fluoride treatments can help restore the enamel and reverse the damage.
Fillings
When cavities have formed, dentists remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill the area with a dental material, such as composite resin or amalgam.
Crowns
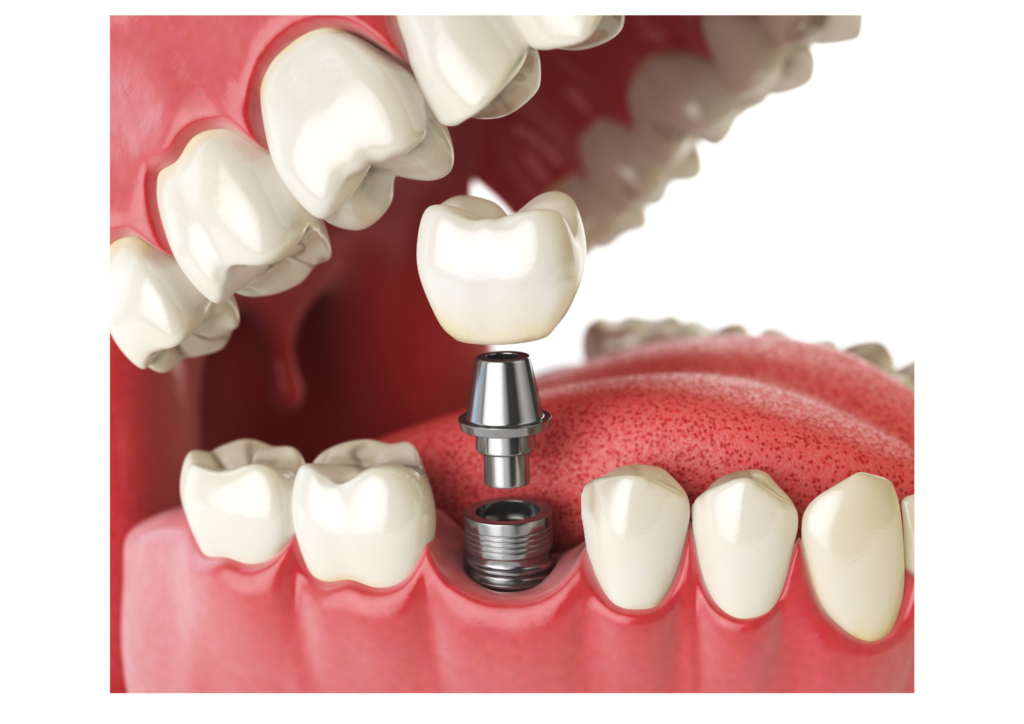
For extensive decay that weakens the tooth, a crown may be necessary to restore its strength and function.
Root Canals
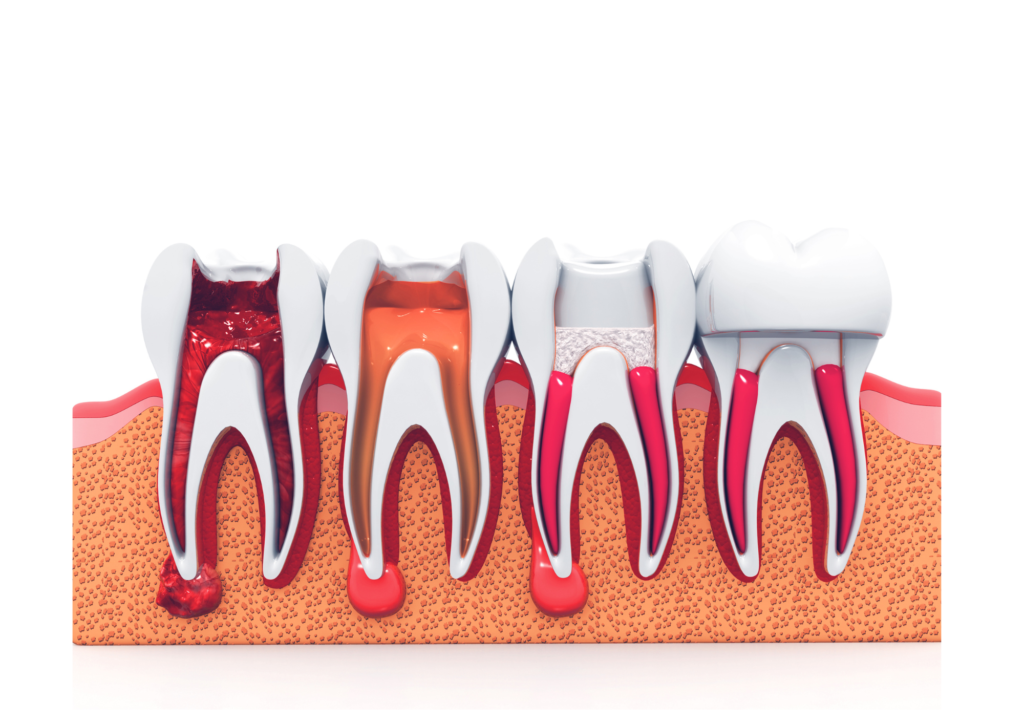
If the decay reaches the tooth’s pulp, a root canal may be needed to remove the infected tissue and save the tooth.
Tooth Extractions
In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Cavities
Foods to Avoid
Limiting sugary snacks, candies, and acidic beverages can reduce the risk of cavities.
Foods That Promote Dental Health
Foods rich in calcium and phosphorus, such as cheese, milk, and leafy greens, can help strengthen the enamel.
Importance of Water
Drinking water, especially fluoridated water, helps rinse away food particles and acids, promoting a healthier mouth.
Importance of Fluoride in Preventing Cavities
How Fluoride Works
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel by remineralizing areas that have been demineralized by acids.
Sources of Fluoride
Fluoride can be found in toothpaste, mouth rinses, and drinking water, as well as in professional treatments provided by dentists.
Fluoride Treatments
Dentists can apply fluoride treatments in the form of gels, foams, or varnishes to provide extra protection against decay.
The Impact of Oral Hygiene on Cavities
Proper Brushing Technique
Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and brushing for at least two minutes twice a day can effectively remove plaque and prevent cavities.
Importance of Flossing
Flossing daily helps remove food particles and plaque from between teeth and along the gumline, areas that a toothbrush cannot reach.
Use of Mouthwash
Antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and plaque, providing an additional layer of protection against cavities.
The Role of Regular Dental Visits
Professional Cleanings
Dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar that cannot be eliminated by regular brushing and flossing, helping to prevent cavities.
Early Detection and Treatment
Regular dental visits allow for early detection of cavities and other dental issues, enabling prompt treatment before problems worsen.
Customized Dental Care Advice
Dentists can provide personalized advice and recommendations for maintaining optimal oral health based on individual needs.
Home Remedies for Early Stage Cavities
Oil Pulling
Oil pulling, an ancient Ayurvedic practice, involves swishing oil (like coconut oil) in the mouth for about 20 minutes to reduce bacteria and improve oral health.



